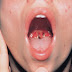
Pharyngitis or tonsillitis is inflammation of the pharynx or tonsils.
Physical finding and Clinical presentation
 |
| Adenoviral Pharyngitis |
- Pharynx
- May appear normal to severely erythematous
- Tonsillar hypertrophy and exudates commonly seen but do not indicate cause.
- Viral infection
- Rhinorrhea
- Conjunctivitis
- Cough
- Bacterial infection, especially group A Streptococcus
- High fever
- Systemic signs of infection
- Herpes simplex or enterovirus infection: vesicles
- Streptococcal infection
- Rare complications
- Scarlet fever
- Rheumatic fever
- Acute glomerulonephritis
- Extension of infection: tonsillar, parapharyngeal, or retropharyngeal abscess presenting with severe pain, high fever, trismus.
Viruses
- Respiratory syncytial virus
- Influenza types A and B
- Epstein-Barr virus
- Adenovirus
- Herpes simplex
- Streptococcus
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Arcanobacterium haemolyticum
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Chlamydia pneumoniae
- Sore throat associated with granulocytopenia, thyroiditis
- Tonsillar hypertrophy associated with lymphoma.
- Throat swab for culture to exclude S. pyogenes, N. gonorrhoeae (requires specifi c transport medium)
- Rapid streptococcal antigen test (culture should be performed if rapid test negative and diagnosis suspected)
- Monospot
- CBC with differential
- May help support diagnosis of bacterial infection
- Streptococcal infection suggested by leukocytosis of more
than 15,000/mm3
- Viral cultures, serologic studies rarely needed
- Seldom indicate
- If streptococcal infection proved or suspected:
- Penicillin
- Erythromycin if penicillin allergic
- If gonococcal infection proved or suspected: ceftriaxone
- Tonsillopharyngitis is generally managed in an outpatient setting with follow-up arranged in a week or two. Admission to the hospital is indicated for local suppurative complications (peritonsillar abscess, lateral pharyngeal or posterior pharyngeal abscess, impending airway closure, or inability to swallow food, medications, or water).
 |
| Pharyngitis associated with GAS (Group A strep) infection |