Nutrients are organic and inorganic molecules that support the growth and survival of a living organism. Those utilized by humans can be divided into six major classes: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, vitamins, water, and minerals. Nutrients are used for three major purposes:
- To supply the energy needed for the body to perform work
- To provide the building blocks for the synthesis of other important molecules.
- To support the function of metabolic pathways
The energy content of nutrients is an expression of the amount of heat released upon burning 1 g of a nutrient. This energy is measured in kilocalories (kcal); however, it is conventionally expressed as “calories” on the Nutrition Facts labels of foods. The energy content for the major energy nutrients are as follows:
- Carbohydrates: 4.1 kcal/g The energy content of nutrients is an expression of the amount of heat released upon burning 1 g of a nutrient. This energy is measured in kilocalories (kcal); however, it
- Proteins: 4.1 kcal/g
- Lipids: 9.3 kcal/g
The daily energy requirements are met through the consumption of food. The Food and Nutrition Board (Institute of Medicine, National Academies) has defined the following terms as part of the Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) values for the six major groups of nutrients:
- Adequate intake (AI) is a recommended average daily nutrient intake level assumed to be adequate based on observed or experimentally determined estimates of daily nutrient intake by a group (or groups) of healthy people. AI is used when an RDA cannot be determined (e.g., for certain minerals).
- Tolerable upper intake level (UL) is the highest average daily nutrient intake level likely to pose no risk of adverse health effects to almost all individuals in a particular life stage and gender group. As intake increases above the UL, the potential risk of adverse health effects increases.
- Estimated average requirement (EAR) is the average daily nutrient intake level estimated to meet the requirement of 50% of the healthy individuals in a particular life stage and gender group.
- Recommended dietary allowance (RDA) is a value that represents the amount of a nutrient that, if consumed by every member of a population, will keep 98% of individuals (of a particular life stage and gender group) in good health.
Total energy expenditure is the amount of calories needed to meet the body's energy demands. It is dependent on age, weight, gender, diet, physical activity, and overall health, which are expressed in the following terms:
- Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the amount of calories required to maintain normal physiological functions when the body is at rest and accounts for 60 to 70% of total energy expenditure. BMR varies with gender, age, health, and hormone levels and is estimated using a formula that takes these factors into account.
- Thermic effect of food (TEF) represents the amount of calories consumed during the digestion, absorption, and metabolism of nutrients. It accounts for ~10% of total energy expenditure.
- Physical activity level (PAL) accounts for the amount of calories required to support certain levels of physical exertion. It is expressed in values that range from 1.2 to 2.4. The lowest value represents the PAL of individuals engaged in no physical activity (e.g., bedridden persons); the highest value represents that of individuals engaged in strenuous forms of physical activity(e.g., performance athletes).
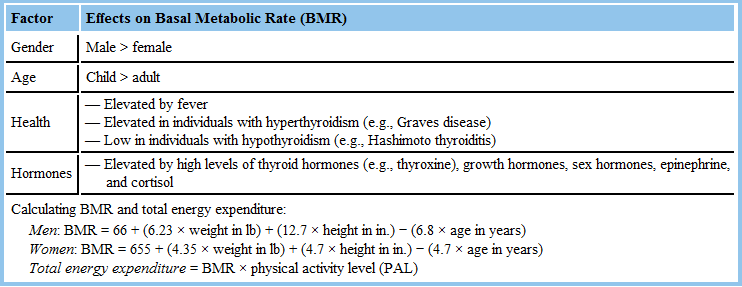 |
| Factors that Influence Basal Metabolic Rate and Its Use in Calculating the Total Energy Expenditure. |