HIV Infection
Definition
HIV infection is a disease caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The condition gradually destroys the immune system, which makes it harder for the body to fight infections.
Cause & Risk Factor
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) can be spread by the following:
- Contaminated blood transfusions and blood products
- Intimate sexual contact
- The use of contaminated needles and syringes
The virus may also spread from a mother to her baby, either at birth or through breastfeeding.
People who become infected with HIV may have no symptoms for up to 10 years, but they can still pass the infection to others. After being exposed to the virus, it usually takes about 3 months for the HIV ELISA blood test to change from HIV negative to HIV positive. HIV has spread throughout the US. The disease is more prevalent in urban areas, especially in inner cities.
Symptoms & Signs
Symptoms related to HIV are usually due to an infection in part of the body. Some symptoms related to HIV infection include:
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Frequent vaginal yeast infections
- Headache
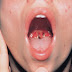
- Mouth sores, including fungal (candida) infection
- Muscular stiffness or aching
- Rash of various types, including seborrheic dermatitis
- Sore throat
- Swollen lymph glands
If You Enjoyed This, Take 5 Seconds To Share It